This tutorial shows how you can build your own custom template for the PDF invoices in the ISPConfig billing module. The custom template will be update-safe, so you don't have to worry that your modifications will vanish on ISPConfig or Billing Module update.
What we will do
I will create a new custom template with the name "mycompany" and set this template as the default template for new invoices, proforma invoices and credit notes.
The Basics
The templates for the PDF files that get created by the ISPConfig Billing Module are in the folder:
/usr/local/ispconfig/interface/web/billing/templates/pdf_invoice
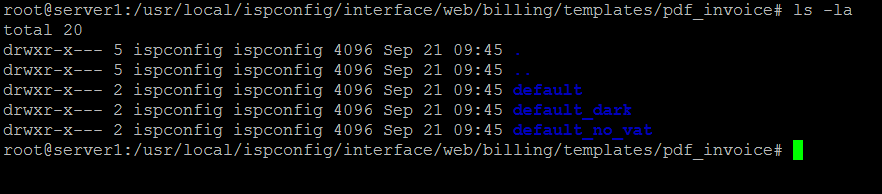
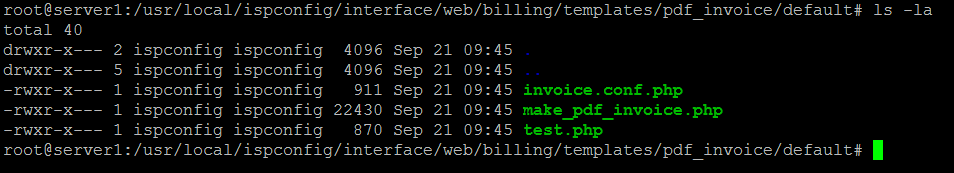
Each template has it's own folder, the folder name is the name of the template. Please note that the folder name has to be in lowercase letters and it may not contain whitespaces. Instead of a whitespace, you can use an underscore "_" in the folder name.
Here is a screenshot how the folder with the default templates looks like.
![]()
The structure of the files in these folders is always the same. I'll show it below for the default template.
![]()
The file invoice.conf.php contains the base settings of the invoice like fonts, background color, and column widths. The file make_pdf_invoice.php is the actual PDF template, it contains the code that creates the invoice. The file test.php can be used to test the invoice. In that file, you can set the ID of an invoice that shall be rendered directly in the browser.
Create a custom invoice template in ISPConfig Billing Module
Let's get started with the new invoice template. I will use the "default" template as the basis.
Make a copy of the default template and name it "mycompany".
cp -prf /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/web/billing/templates/pdf_invoice/default /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/web/billing/templates/pdf_invoice/mycompany
Then go to the new folder:
cd /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/web/billing/templates/pdf_invoice/mycompany
and edit the make_pdf_invoice.php file.
nano make_pdf_invoice.php
Near the top of the file, you will find this line:
class PDFInvoice_default extends tFPDF
The word default in that line refers to the name of the invoice template. Change the line to:
class PDFInvoice_mycompany extends tFPDF
so that the name matches the on that you have chosen for your template.
Next, open the test.php file:
nano test.php
Set the ID of the invoice that you like to render for test purposes in line 11. The ID refers to the column invoice_id of the database table invoice in the ISPConfig database. In line 20, exchange the word default with the name of your invoice template. In case of this example, the line will be like this:
$pdf = new PDFInvoice_mycompany();
Activate the invoice template in ISPConfig
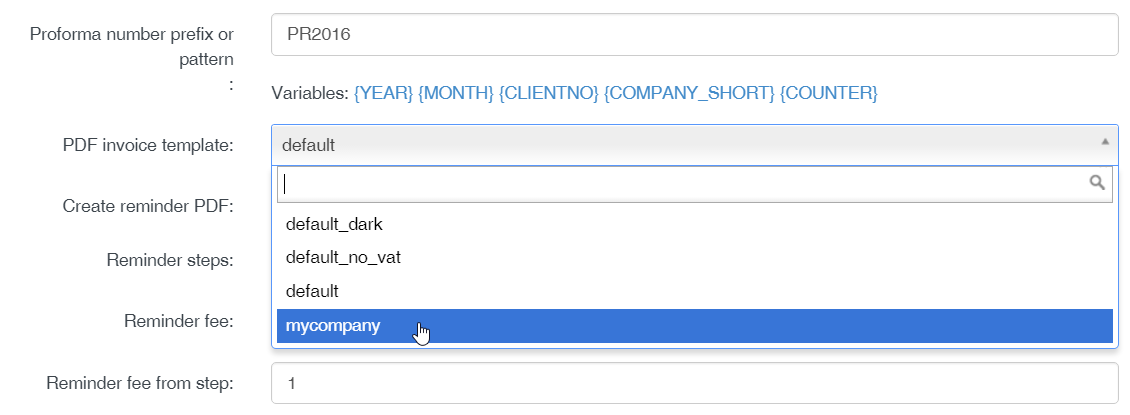
Login to ISPConfig as admin user, go to the billing module. There you click on Settings > Company in the left menu to edit the company details. Select your custom invoice template in the PDF invoice template field:
![]()
Now you can start making adjustments in the:
/usr/local/ispconfig/interface/web/billing/templates/pdf_invoice/mycompany/make_pdf_invoice.php
file to customize the invoice. The code in this file is commented, so you should easily find the places where you can adjust headline, address field etc. in your template.
Testing
There are several ways to test your new template. One way is that you open the details of an existing invoice (or create a new one) and press the "Save and finalize" button, this will create a new invoice based on your custom template. Then click on the PDF download icon to download or view it.
This procedure might become a bit annoying when you want to do extensive edits. That's why we made the test.php file for. Login to ISPConfig as admin.
To use test.php, login to ISPConfig as admin user (test.php will not work without login), then modify the URL in the browser to point to the test file. Example:
https://server1.example.com:8080/billing/templates/pdf_invoice/mycompany/test.php
and press return. The invoice with the ID that you configured in the test.php file will get rendered with your new template directly in the browser. Just press reload after editing the make_pdf_invoice.php file the latest changes you made in the template.
The post How to create a custom invoice template in ISPConfig 3 Billing Module appeared first on FAQforge.